Nonbank financial institutions (NBFIs) vary from country to country by types of providers, options for using the services, and presence in the market. In some countries, they may resemble traditional banks in all but name; in others, they may be niche institutions that provide financial services specific to key demographic groups, such as the agricultural sector. In most markets, microfinance institutions (MFIs) serve as one type of NBFI. In Bangladesh, especially, MFIs and NBFIs in general became very prominent after introducing the concept of microloans. However, in recent years, since 2016, banks and mobile money services have become more prominent – and reducing the prevalence of NBFIs. Similarly, in many other countries, NBFIs’ relevance is declining compared to the bank and mobile money markets.
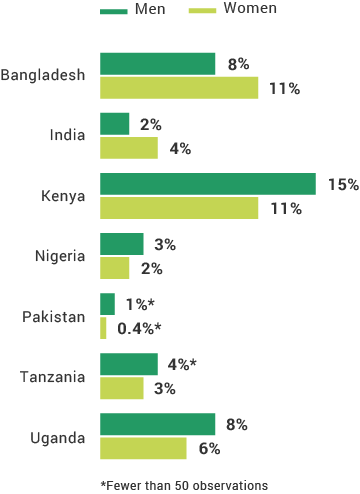
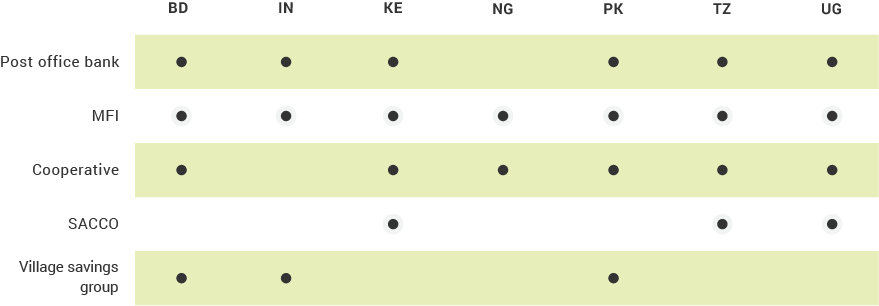
Post office banks, cooperatives, and savings and credit cooperative organizations (SACCOs) are common forms of NBFIs operating in the FII program countries. NBFIs often serve similar numbers of women and men, making them an especially important component to inclusion. In many of the FII countries, women are as likely to have access to NBFIs as men, while being much less likely to have access to a bank. However, across many of the FII countries, more rural and below poverty individuals than their counterparts access NBFIs than mobile money or banks.
Use of Nonbank Financial Institutions
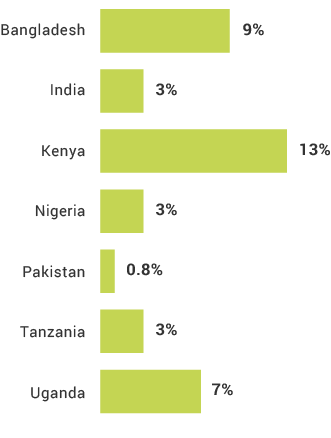
Registered Account Holders by Gender
The Nonbank Financial Institutions (NBFI) Indicator

True or false
Bangladesh is often associated with the rise of microfinance.
Which services are NBFIs most often associated with?
True or false
Financial inclusion in Pakistan is primarily through nonbank financial institutions (NBFIs).
True or false
NBFIs are regulated in Uganda.