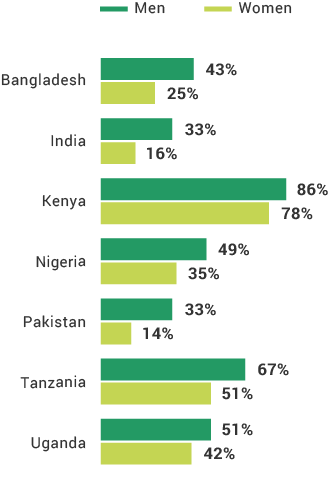
The financial inclusion insights surveys in Africa have shown that the mobile phone is the most effective digital channel for expanding lower-income populations’ access to formal financial services. Nine in 10 Kenya adults and four in five adults in Tanzania and Nigeria have mobile phone and SIM card access. Comparing FII countries, more mobile phone users in Africa use their phones for advanced services than do those in Asia. The least likely groups to own mobile phones across FII countries are females, rural residents, and the poor, which is a barrier to digital financial services uptake. As more people across the globe begin to use mobile phones and digital financial services, providers will have a wider opportunity to know their customers digitally and offer them products better suited to their needs.
Mobile Phones Access and Ownership
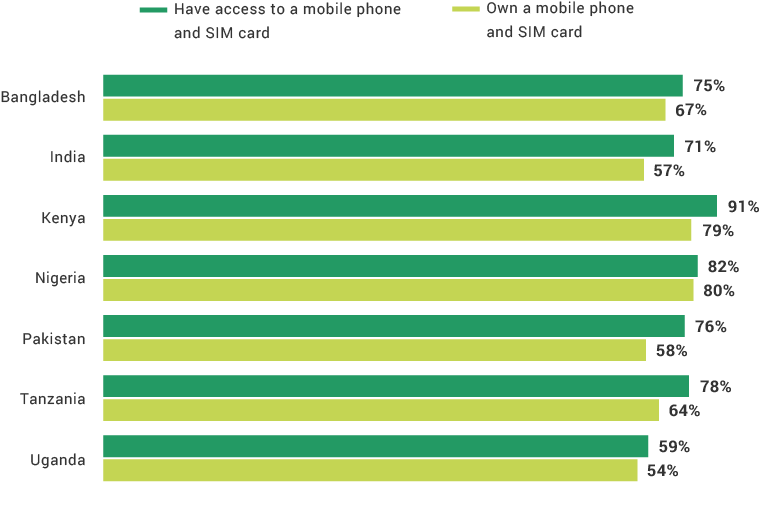
Ownership by Demographic
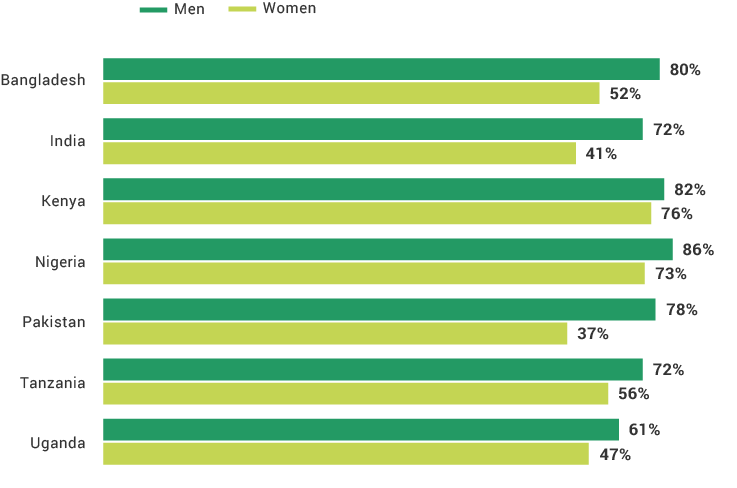
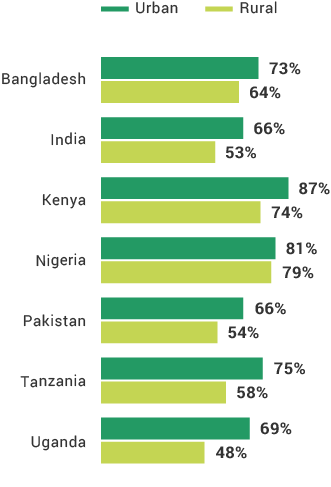
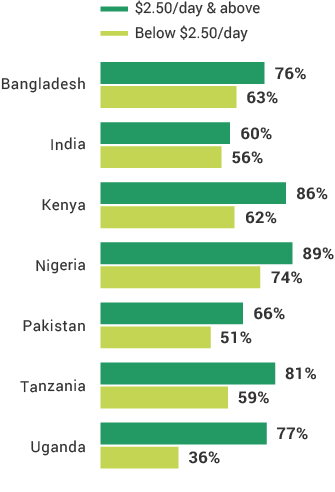
Use of Mobile Phones for Advanced Functions
True or false
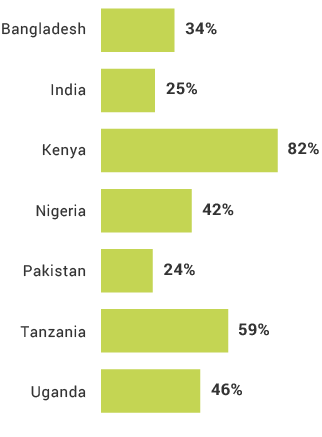
Among FII countries, Uganda has the lowest percentages of adults who own a mobile phone and SIM card.

True or false
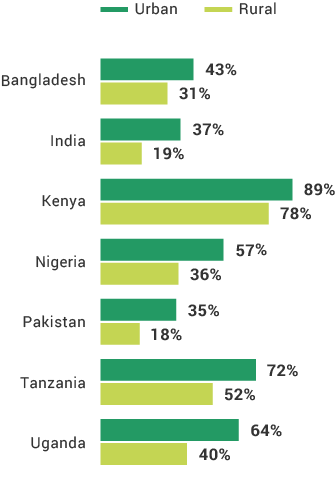
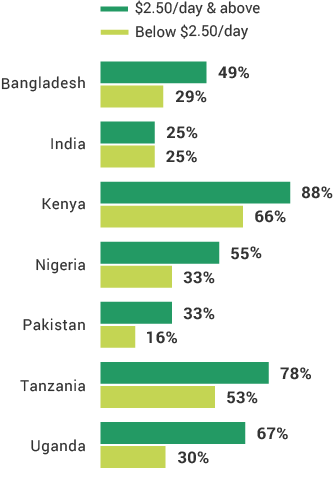
In Uganda, those who are more likely to use their phones for advanced services are those living above the poverty line and urban residents.
What percentage of adult Ugandan phone users have a smart phone?

True or false
In 1973, Motorola was the first company to develop a prototype for the handheld mobile phone.
True or false
The percentage of adult urbanites who use advanced mobile phone functions is the same in Kenya and Tanzania.